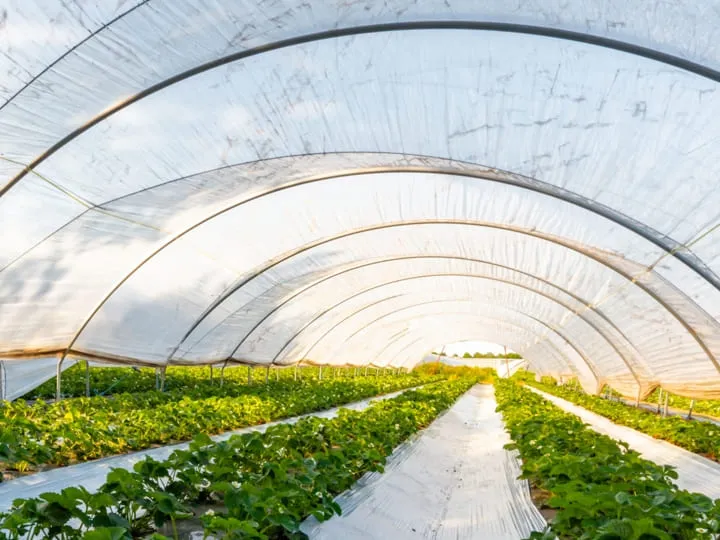
أفلام الزراعة، مثل أفلام المولش وأفلام البيوت المحمية، هي مواد لا غنى عنها في الزراعة الحديثة. إنها تحسن بشكل فعال بيئة نمو المحاصيل وتزيد من غلة الزراعة.
ومع ذلك، يمكن أن يؤدي التخلص غير السليم من الأفلام الزراعية إلى تلوث بيئي شديد. إن إعادة تدوير الأفلام الزراعية لا تقلل فقط من التأثير البيئي ولكنها تسهل أيضًا إعادة استخدام الموارد، مما يوفر فوائد اقتصادية وبيئية كبيرة. تستكشف هذه المقالة التحديات والأساليب.
ما هو الفيلم الزراعي؟
فيلم زراعي هو نوع من الأغطية البلاستيكية المستخدمة في الزراعة والبستنة لتعزيز إنتاجية المحاصيل وحماية النباتات. مصنوعة من مواد مثل البولي إيثيلين (PE) أو البولي بروبيلين (PP)، تخدم هذه الأفلام أغراضًا متنوعة، مثل:
- التغطية
- الصوبات الزراعية
- أغلفة السيلاج
- أغطية الصفوف

التحديات في إعادة تدوير الفيلم الزراعي
مشاكل التلوث
غالبًا ما تتعرض الأفلام الزراعية للحقول لفترات طويلة، مما يؤدي إلى تراكم الأوساخ والمبيدات الحشرية والأسمدة وغيرها من الملوثات على أسطحها. تزيد هذه الملوثات من صعوبة إعادة التدوير والمعالجة.
التقادم والتلف
تميل الأفلام الزراعية التي تم استخدامها لفترات طويلة إلى التقدم في العمر وتصبح هشة، خاصة عند تعرضها لأشعة الشمس، والمطر، ودرجات الحرارة العالية. قد تنكسر هذه الأفلام إلى شظايا، مما يزيد من تعقيد عملية الجمع والتنظيف.
خلط المواد
تُستخدم مواد مختلفة في الأفلام الزراعية، مثل البولي إيثيلين (PE) والإيثيلين فينيل أسيتات (EVA). تتطلب المواد المختلطة الفرز أثناء عملية إعادة التدوير، مما يزيد من تعقيد وتكلفة العملية.
أنظمة إعادة التدوير غير المكتملة
في العديد من المناطق، لم يتم بعد إنشاء أنظمة إعادة تدوير شاملة للأفلام الزراعية. قد يفتقر المزارعون إلى الوعي بممارسات إعادة التدوير، مما يؤدي إلى تشتت الأفلام المهدرة عبر الحقول، مما يجعل جمعها المركزي أكثر صعوبة.
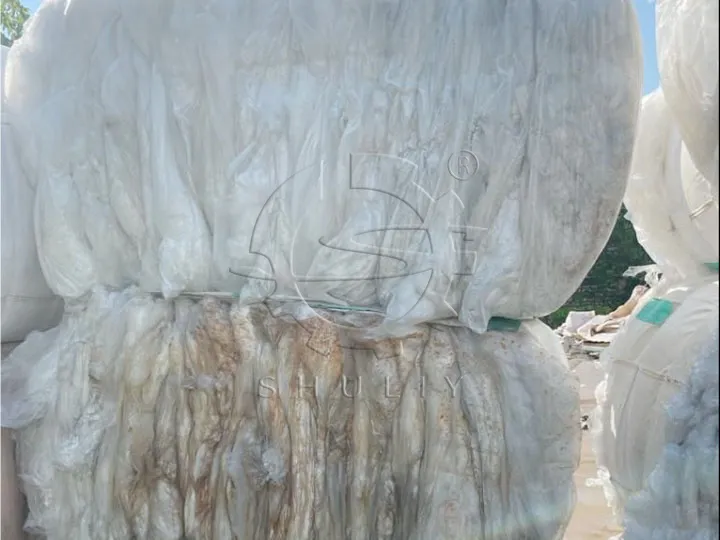

طرق إعادة تدوير الأفلام الزراعية
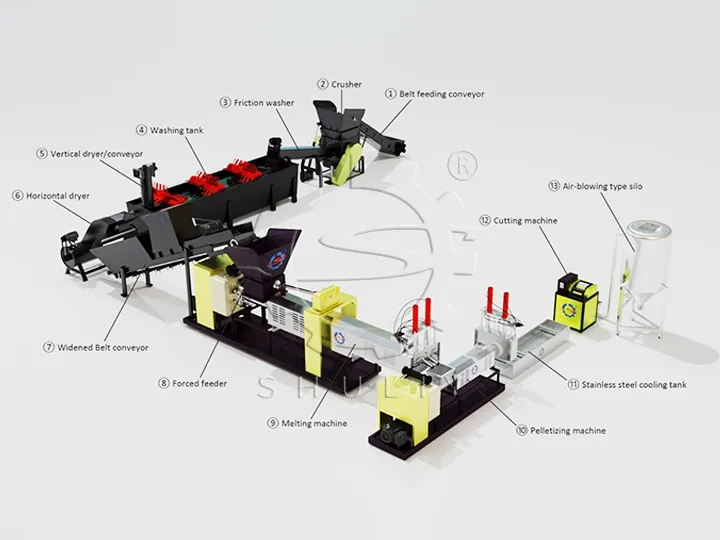
- جمع الحقلتبدأ عملية إعادة التدوير بجمع الأفلام النفايات من الحقول. يجب على المزارعين تنظيف وتخزين الأفلام بسرعة بعد حصاد المحاصيل.
- الفرزتحتاج الأفلام المجمعة إلى الفرز لفصل المواد المختلفة والأفلام الملوثة بشدة.
- التقطيع: يتم أولاً سحق الفيلم من خلال آلة التمزيق إلى قطع صغيرة الحجم للتنظيف والتكوير اللاحق.
- غسلثم يتم إزالة التربة والمبيدات الحشرية والملحقات الأخرى عن طريق غسل المعدات لضمان جودة المعالجة اللاحقة.
- تجفيفبعد ذلك، تُستخدم آلات إزالة الماء أو معدات التجفيف لتقليل محتوى الرطوبة استعدادًا للتكوير.
- التحبيبات وإعادة الاستخدام: يتم تغذية قطع الفيلم المعالجة في آلات تكوير، حيث يتم صهرها وضغطها إلى كريات بلاستيكية معاد تدويرها. يمكن استخدام هذه الكريات في تصنيع أفلام زراعية جديدة، وأنابيب بلاستيكية، ومواد تعبئة، والمزيد، مما يكمل دورة إعادة استخدام الموارد.
فوائد إعادة تدوير الأفلام الزراعية
الفوائد البيئية
إعادة تدوير الأفلام الزراعية تقلل من النفايات البلاستيكية المتروكة في الحقول، مما يمنع تلوث التربة والأضرار البيئية. كما أنها تخفف من التأثير البيئي السلبي الناتج عن حرق أو دفن النفايات البلاستيكية.
القيمة الاقتصادية
يمكن معالجة الأفلام الزراعية المعاد تدويرها إلى مواد خام بلاستيكية عالية القيمة، مما يقلل من تكاليف الإنتاج ويوفر فوائد اقتصادية للمزارعين وشركات إعادة التدوير.
باختصار، من الصعب إعادة تدوير الأفلام الزراعية، ولكن يمكن إعادة تدويرها بفعالية باستخدام طريقة التكوير الصحيحة.






